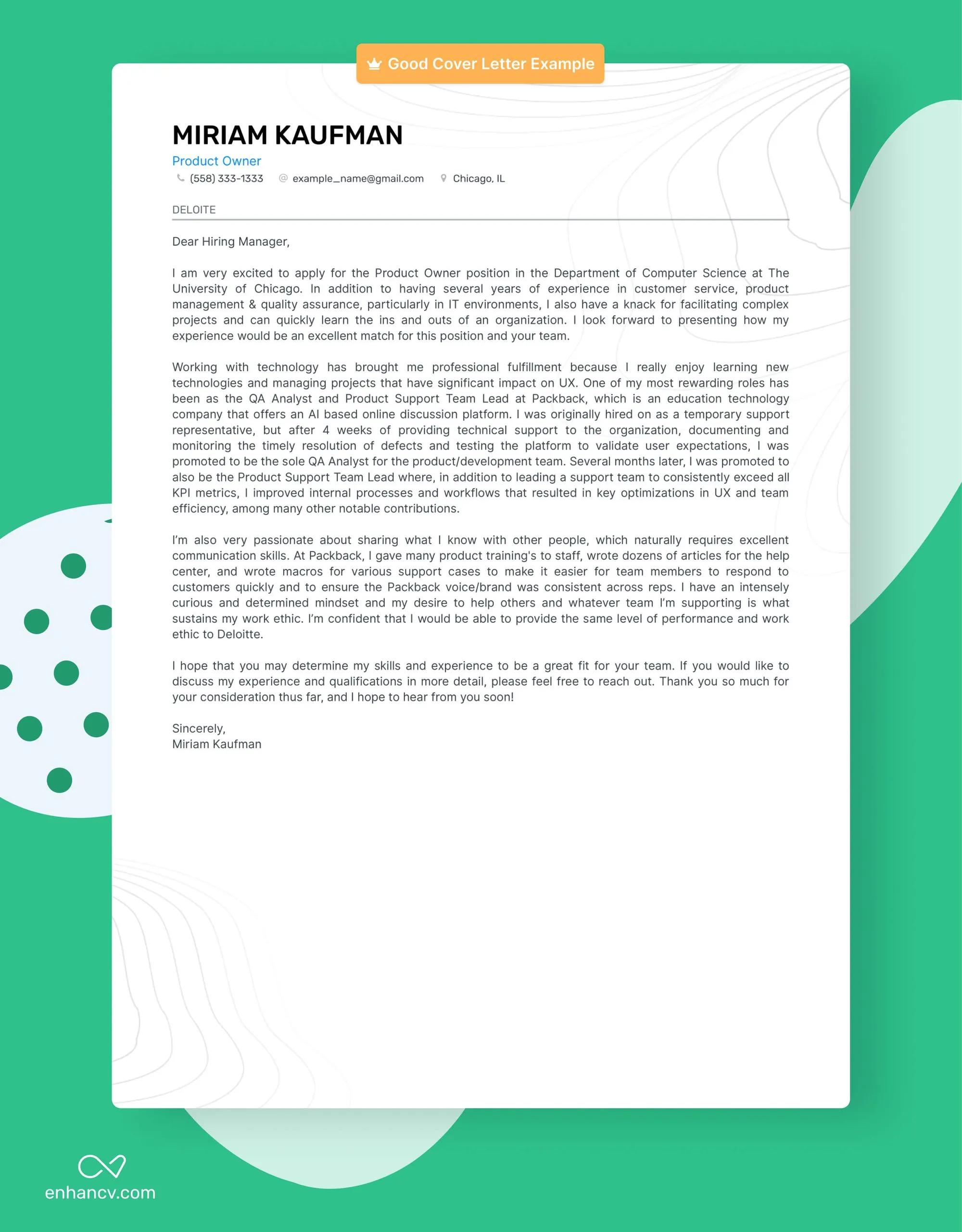
What is a Cover Letter?
A cover letter is a one-page document you submit with your resume when applying for a job. It serves as a personal introduction, allowing you to elaborate on your qualifications, skills, and experiences. The primary goal is to express your interest in the position, highlight why you’re a good fit, and encourage the hiring manager to read your resume. Unlike a resume, which provides a summary of your professional background, a cover letter allows you to explain your motivations and connect your experiences to the specific job requirements. It’s your opportunity to make a strong first impression and showcase your personality and communication skills.
Purpose of a Cover Letter
The primary purpose of a cover letter is to introduce yourself to a potential employer and demonstrate your enthusiasm for the role and the company. It bridges the gap between your resume and the job description, illustrating how your skills and experiences align with the employer’s needs. Furthermore, a cover letter offers a chance to highlight unique aspects of your background or explain any career transitions or gaps in your resume. By personalizing your application, you can make a compelling case for why you’re the ideal candidate and differentiate yourself from other applicants. It is an active way to show, not just tell, that you are the right fit for the role.
Key Components of a Cover Letter

A well-structured cover letter typically includes several key components. Begin with a professional heading that includes your contact information and the date. Next, address the hiring manager by name, if possible, to personalize the letter. The opening paragraph should state the position you’re applying for and express your interest. The body of the letter should highlight your relevant skills and experiences, explaining how they align with the job requirements. Provide specific examples of your accomplishments, quantifying them whenever possible. Conclude with a strong closing paragraph that reiterates your interest and thanks the hiring manager for their time and consideration. Proofread carefully for any grammar or spelling errors.
What is a Resume?
A resume is a concise, structured document summarizing your professional and educational background. Its purpose is to provide a snapshot of your skills, experience, and accomplishments to potential employers. The resume serves as a quick reference guide, enabling employers to assess your qualifications and suitability for a job. Resumes typically include information about your work history, education, skills, and any relevant achievements or certifications. Unlike a cover letter, a resume is generally formatted in a consistent and standardized manner, making it easy for employers to compare different candidates. It is a detailed summary of your qualifications that helps you stand out from other job applicants.
Purpose of a Resume
The main purpose of a resume is to secure an interview. It provides a clear and concise overview of your qualifications, making it easy for employers to assess your suitability for a role. A well-crafted resume highlights your key skills and experiences, demonstrating your ability to meet the requirements of the job. The resume should be tailored to the specific position you’re applying for, emphasizing the most relevant aspects of your background. It acts as a marketing tool, showcasing your professional achievements and presenting you as a valuable candidate. A resume is your initial introduction to the employer, aiming to convince them to learn more about you through an interview.
Key Components of a Resume

A resume typically includes several core sections designed to showcase your qualifications effectively. Start with a clear header that includes your contact information. Include a professional summary or objective statement to provide a brief overview of your skills and career goals. List your work experience in reverse chronological order, detailing your responsibilities and accomplishments for each role. Include an education section that lists your degrees, certifications, and relevant coursework. Add a skills section highlighting your technical and soft skills, and include any additional sections such as projects, awards, or volunteer experience relevant to the job. Customize your resume for each job application, emphasizing the skills and experiences most relevant to the position.
Cover Letter vs Resume Key Differences
The primary differences between a cover letter and a resume lie in their purpose, content, and format. A cover letter is a personalized introduction that explains your interest in a specific role and highlights how your skills and experiences align with the job requirements. In contrast, a resume is a concise summary of your professional and educational background, designed to provide a quick overview of your qualifications. A cover letter allows you to elaborate on your motivations and make a personal connection with the hiring manager. A resume provides a structured presentation of your skills and experience, making it easy for employers to assess your suitability for a role. Both documents are essential for a complete job application, but they serve distinct purposes.
Content and Focus
The content and focus of a cover letter and resume differ significantly. A cover letter focuses on your personality, enthusiasm, and how your skills align with the specific job requirements. It allows you to tell a story, explaining why you are interested in the role and what you hope to achieve. The content is tailored to the job description, highlighting the experiences most relevant to the employer’s needs. A resume, on the other hand, focuses on your professional history, skills, and achievements. It provides a concise overview of your qualifications, emphasizing your experience and accomplishments. The focus is on providing a factual summary of your background, making it easy for employers to evaluate your credentials.
Length and Format
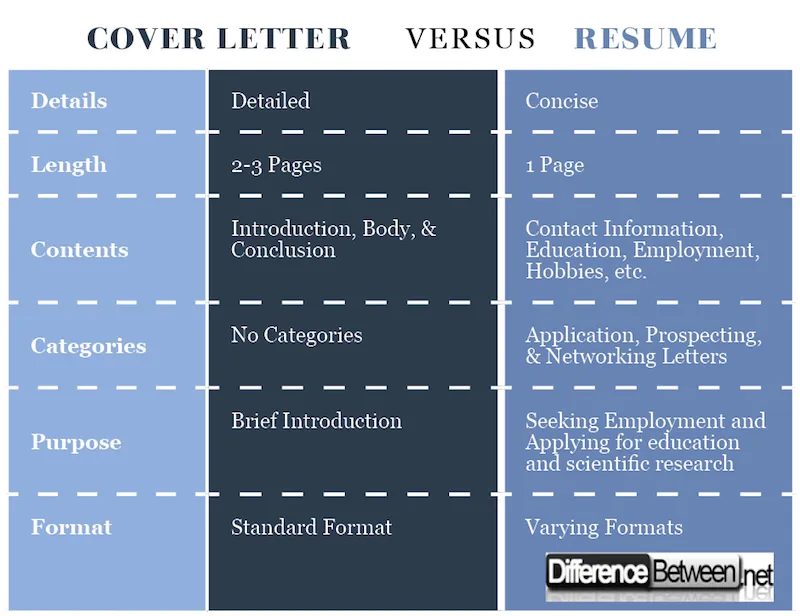
The length and format of a cover letter and resume also differ. A cover letter is typically one page long, allowing you to provide a concise and engaging introduction. The format is less rigid, allowing for a more personal tone and style. The format is designed to highlight the aspects of your personality and why you are the right fit for the role. A resume is generally one to two pages long, depending on your experience. The format is structured and standardized, with clear sections for different types of information. The format is to present information in a clear, easy-to-read manner, making it easy for employers to quickly assess your qualifications.
Target Audience
The target audience for a cover letter and resume is the hiring manager or the person responsible for reviewing applications. However, the approach differs. A cover letter is addressed directly to the hiring manager, allowing you to make a personal connection and demonstrate your enthusiasm for the specific role. You can use a personalized tone and address their needs directly. A resume is designed to be scanned by the hiring manager. The focus is to provide a concise overview of your qualifications, making it easy for them to quickly assess your suitability for a role. The resume needs to be easy to read and highlight the most relevant information.
When to Use a Cover Letter
You should always include a cover letter when applying for a job unless the job posting specifically states otherwise. A cover letter is particularly important when you want to explain career transitions, address any gaps in your employment history, or highlight specific skills and experiences that are relevant to the role. It is especially useful for roles that require strong communication skills or when you want to demonstrate your passion for the company and the position. When the job posting specifically requests a cover letter, it is essential to submit one. Always include a cover letter to make a strong first impression and set yourself apart from other candidates.
When to Use a Resume

A resume is essential for every job application. It provides employers with a quick overview of your qualifications and allows them to assess your suitability for a role. Use your resume to submit your qualifications. It is important to have an updated resume ready and available for every job application. You should customize it for each job you apply for, highlighting the skills and experiences most relevant to the position. A resume should also be readily available if someone asks for your credentials.
How to Write a Cover Letter
To write a compelling cover letter, start by researching the company and the specific role you’re applying for. Personalize your letter by addressing the hiring manager by name, if possible. In the opening paragraph, state the position you’re applying for and express your interest. Highlight your relevant skills and experiences in the body, providing specific examples and quantifying your achievements whenever possible. Show, don’t just tell; support your claims with evidence. In the concluding paragraph, reiterate your interest and thank the hiring manager for their time and consideration. Proofread carefully for any grammar or spelling errors before submitting.
Tips for a Strong Cover Letter
To make your cover letter stand out, tailor it to each job application, highlighting the skills and experiences most relevant to the role. Use action verbs to describe your accomplishments and quantify your achievements whenever possible. Show enthusiasm and passion for the position and the company, demonstrating your interest. Proofread carefully for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure your letter is well-formatted and easy to read. Keep your tone professional and avoid clichés. By following these tips, you can create a cover letter that effectively showcases your qualifications and encourages the hiring manager to review your resume.
How to Write a Resume

To write an effective resume, start with a clear header that includes your contact information. Include a professional summary or objective statement to provide a brief overview of your skills and career goals. List your work experience in reverse chronological order, detailing your responsibilities and achievements for each role. Quantify your accomplishments whenever possible. Include an education section that lists your degrees, certifications, and relevant coursework. Add a skills section highlighting your technical and soft skills, and include any additional sections such as projects, awards, or volunteer experience relevant to the job. Proofread carefully for any grammar and spelling errors.
Tips for a Strong Resume
To make your resume more effective, tailor it to each job application, emphasizing the skills and experiences most relevant to the position. Use action verbs to describe your accomplishments and quantify your achievements whenever possible. Keep your resume concise and easy to read, using clear formatting and bullet points. Use keywords from the job description to ensure your resume passes through applicant tracking systems (ATS). Proofread carefully for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure your resume is free of typos. By following these tips, you can create a resume that effectively showcases your qualifications and helps you get noticed by employers.